The state of Maryland has 57 colleges and universities and more than 151 private career schools. These institutions are overseen at the state level by the Maryland Higher Education Commission (MHEC), which is the state’s higher education coordinating board responsible for establishing statewide policies for Maryland public and private colleges and universities and for-profit career schools. MHEC also administers the state’s financial aid programs. The commission’s 12 members are appointed by the governor.
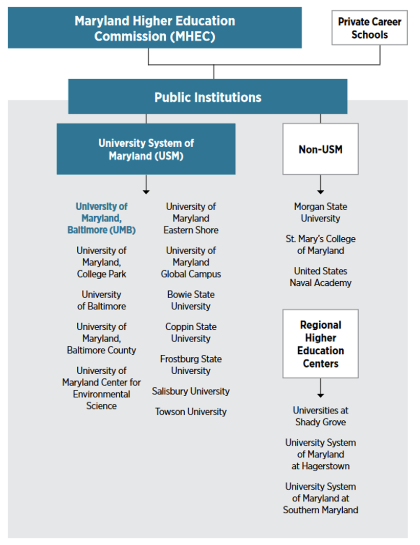
MHEC coordinates the growth and development of postsecondary education in Maryland. In keeping with the goals outlined in the State Plan for Postsecondary Education, the commission establishes statewide policies for public and private colleges and universities, and for private career schools. The commission reviews and approves the start-up and continuation of new colleges and universities in Maryland as well as requests for new academic programs at established schools, including those in the University System of Maryland (USM).
Pursuant to Maryland law, USM is governed by a 21-member Board of Regents (BOR) appointed by the governor, president of the Maryland Senate, and speaker of the Maryland House of Delegates. Seventeen of the members serve staggered five-year terms; two members, by statute, are the Secretaries of Agriculture and Commerce, who serve ex officio as long as they continue in that position; and two members are USM students who serve a one-year term. The BOR is responsible for the governance and management of USM and its constituent institutions, centers, and institutes. It appoints the USM chancellor, who serves as its chief executive officer. The BOR has expressly delegated certain authority to the chancellor and the presidents of the constituent institutions.
UMB is a constituent institution of the USM. An independent unit of state government, the USM is Maryland’s public higher education system. It comprises 12 institutions and three regional higher education centers, offering over 1,000 undergraduate and graduate/professional degree programs to 171,130 students at 120 sites worldwide. USM is the 15th-largest university system in the nation. This dynamic system of leadership and governance enables UMB to fully realize its mission and goals.
The BOR, in consultation with the USM chancellor, appoints the president of UMB, who serves as the chief executive officer. The president of UMB appoints the deans of the professional schools, who report directly to the president. The dean of the graduate school, also appointed by the president, reports to the provost. The president of UMB also appoints administrative officers of the University, including the provost.



